Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
Introduction
An Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is a specialized hospital area designed for the management of critically ill patients who require continuous monitoring, advanced life support, and multidisciplinary care. ICU provides 24×7 observation and immediate intervention to prevent mortality and complications. ICU care is technology-driven, protocol-based, and requires highly trained staff.
Functions of ICU
A. Clinical Functions
Continuous monitoring of vital parameters (ECG, BP, SpO₂, RR, temperature)
Mechanical ventilation and airway management
Hemodynamic monitoring (CVP, arterial line)
Administration of inotropes, vasopressors
Management of organ failure (renal, cardiac, respiratory, neurological)
Post-operative monitoring (especially major surgeries)
Trauma and emergency stabilization
B. Supportive Functions
Infection control and isolation
Pain and sedation management
Nutritional support (enteral/parenteral)
Family counseling and communication
End-of-life care (if required)
Types of ICU
1. General ICU

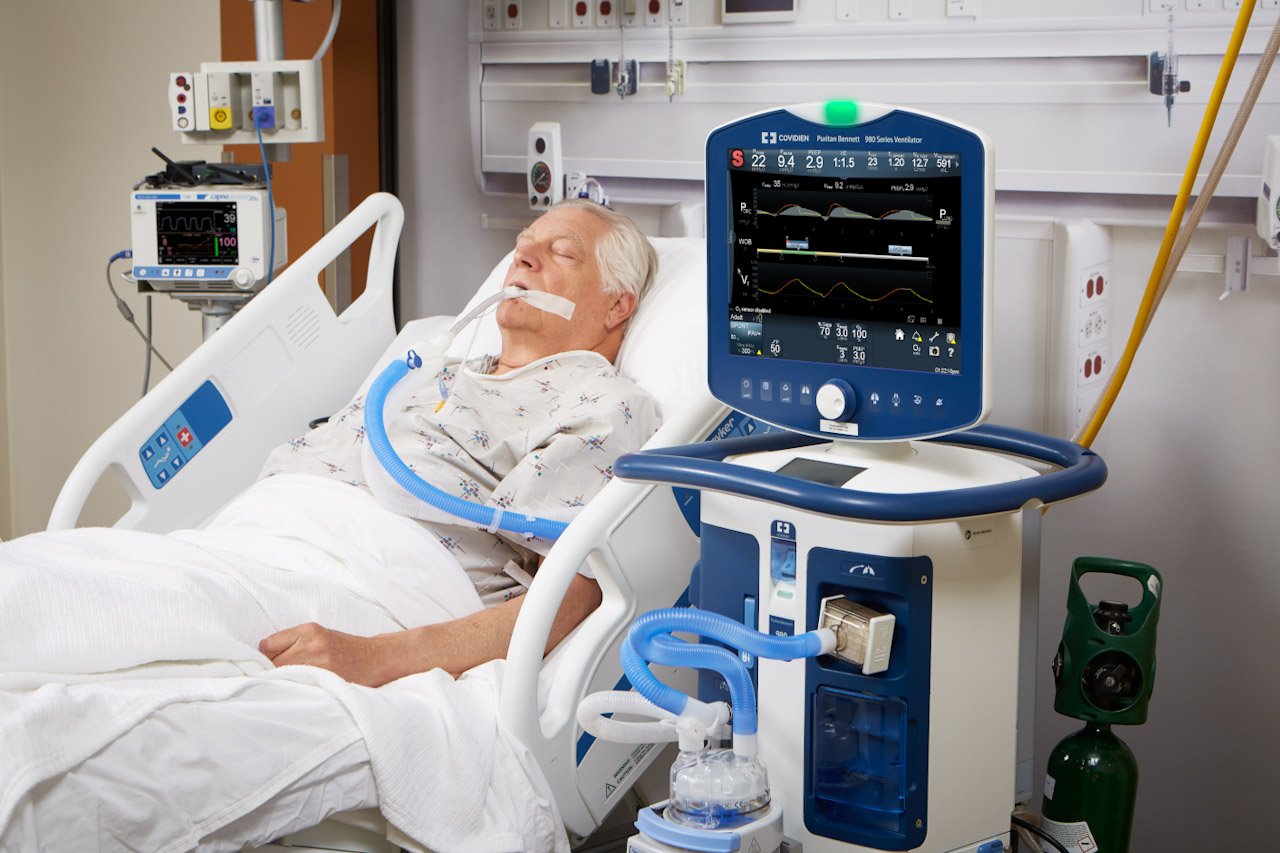
Manages mixed medical and surgical cases
Suitable for multi-specialty hospitals
2. Medical ICU (MICU)
For medical emergencies (sepsis, ARDS, poisoning)
3. Surgical ICU (SICU)
Post-operative and surgical complications
4. Cardiac ICU (CCU)
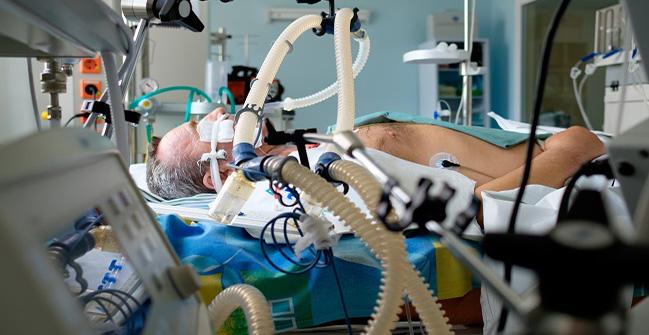
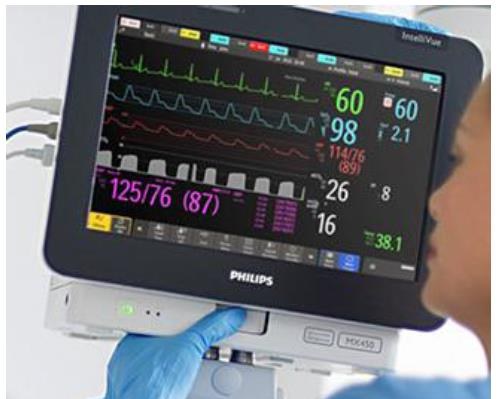
For myocardial infarction, arrhythmias
Advanced cardiac monitoring
5. Neonatal ICU (NICU)

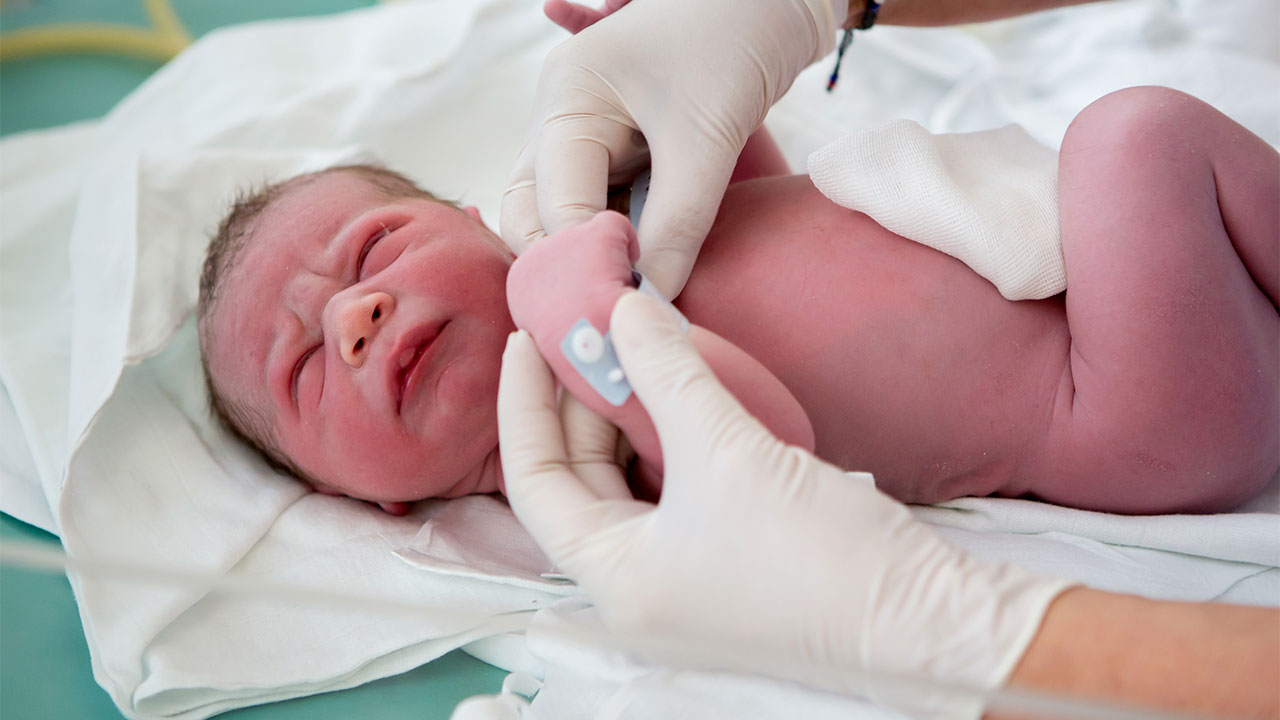

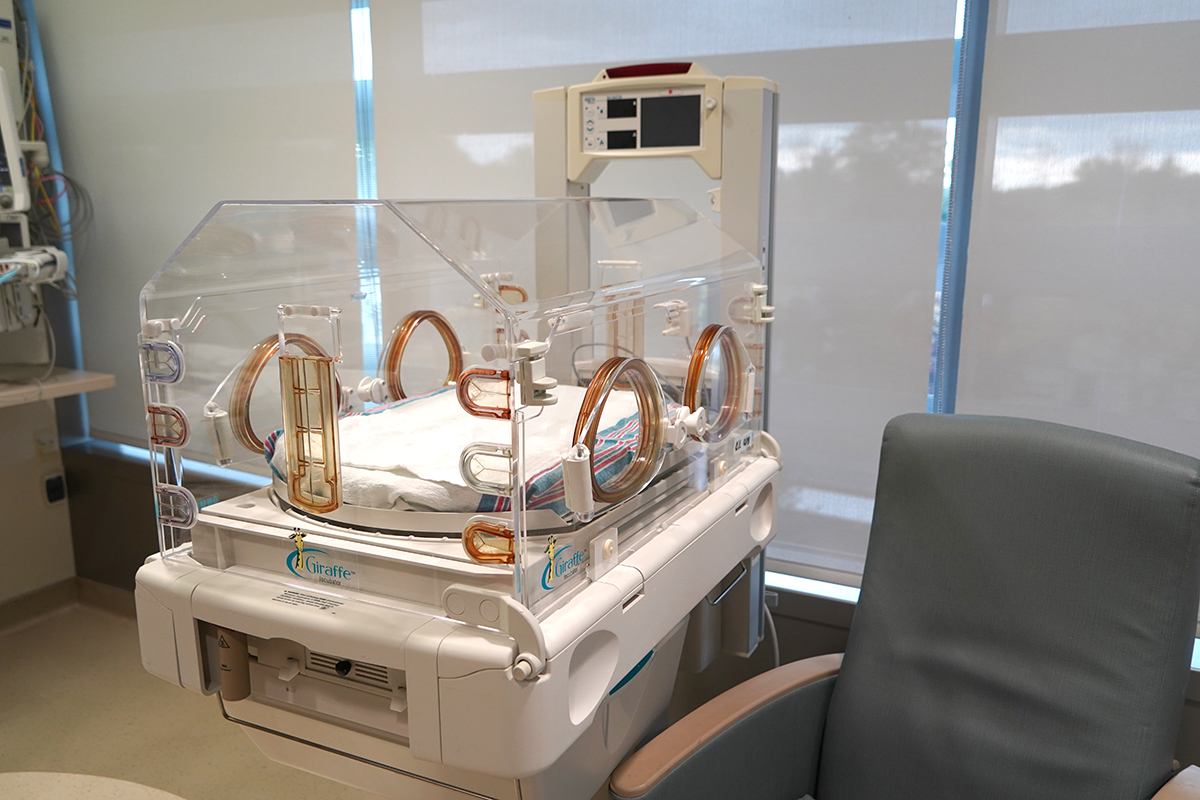
For premature and critically ill newborns
6. Pediatric ICU (PICU)
For critically ill children
7. Trauma ICU
For accident and injury patients
Criteria for Selection of Patient for ICU
Admission Criteria
Respiratory failure requiring ventilator
Hemodynamic instability (shock)
Multi-organ failure
Severe sepsis
Post-major surgery
Unconscious patients (GCS < 8)
Cardiac arrest survivors
Exclusion Criteria
Terminal illness with no benefit from ICU
Stable patients manageable in ward
Layout & Design of ICU
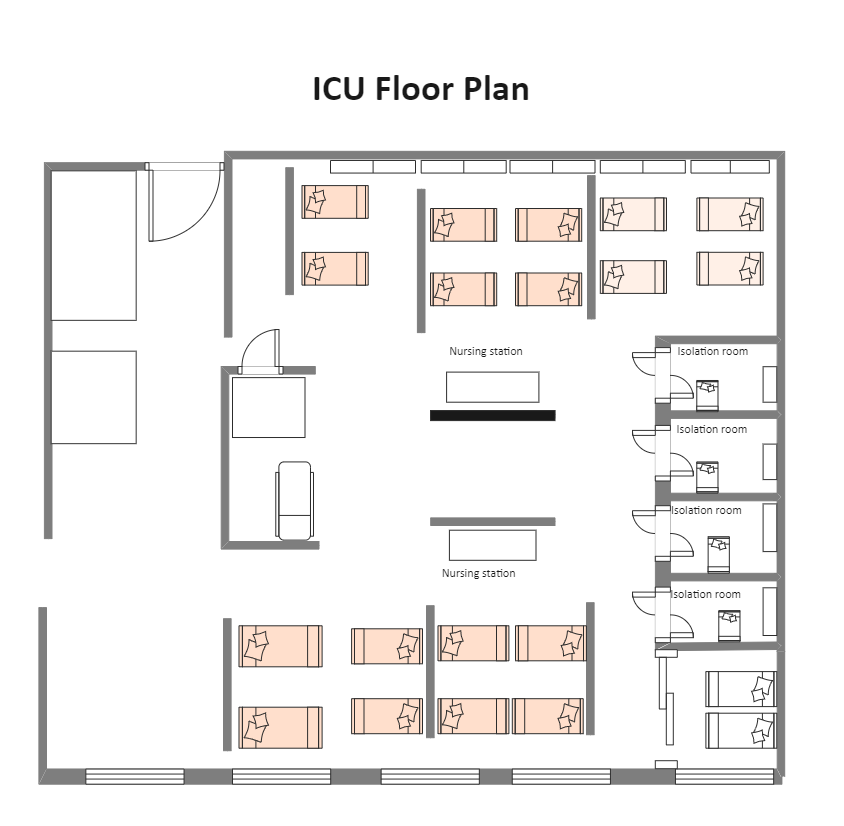

Location
Near Emergency Department and OT
Easily accessible from diagnostic areas
Design Features
Central nursing station
150–200 sq. ft. per bed (recommended)
8–12 beds per unit (ideal)
Isolation rooms with negative pressure
Glass partitions for visibility
Zoning
Patient care area
Nursing station
Clean utility area
Dirty utility area
Equipment storage
Relatives waiting area
Physical Facilities Required
Central oxygen supply
Compressed air
Vacuum system (suction)
Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS)
Generator backup
HVAC with HEPA filters
Adequate lighting (300–500 lux)
Handwashing stations
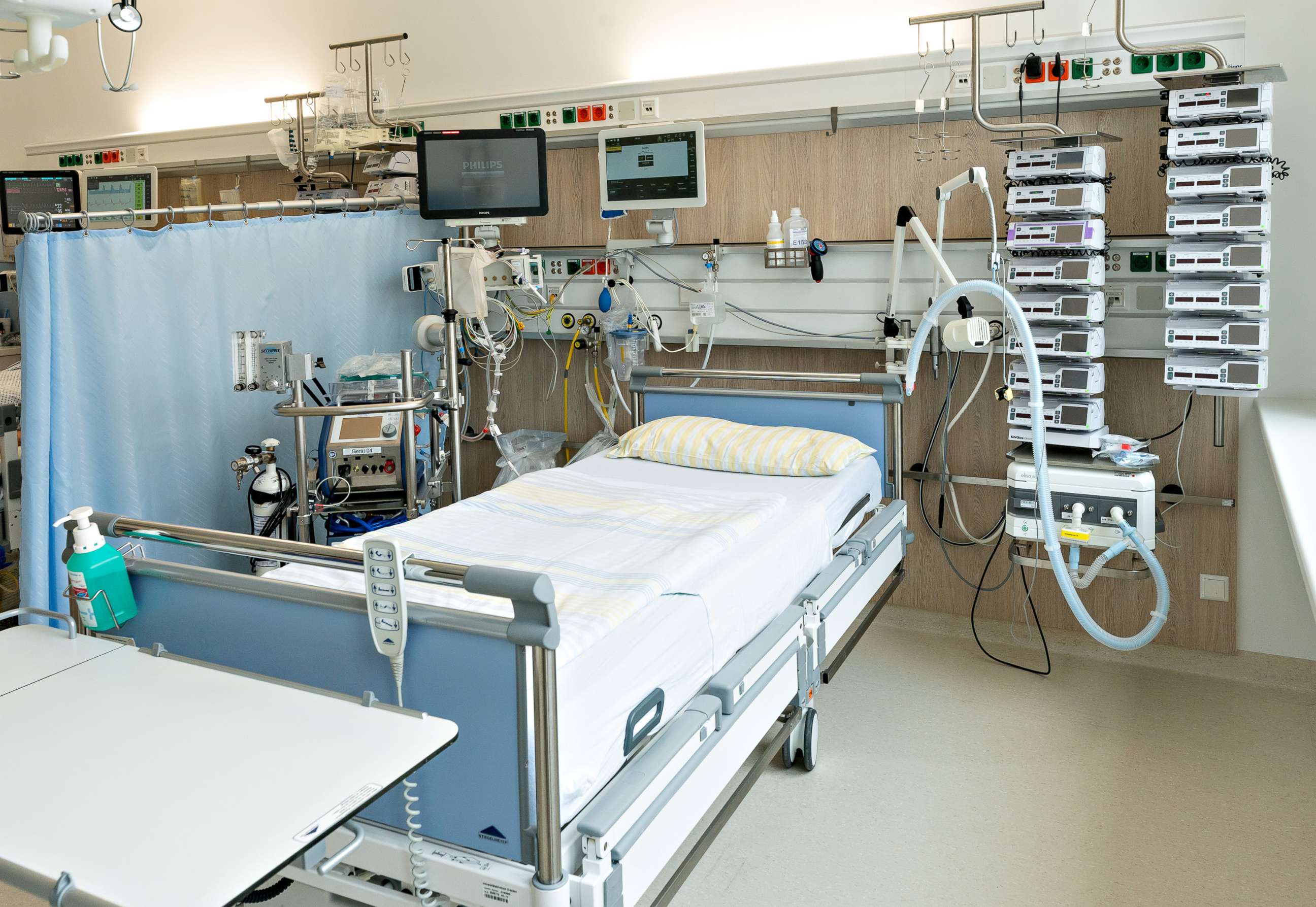
Equipment Required in ICU
Bedside Equipment
ICU beds (adjustable)
Multi-parameter monitors
Syringe pumps & infusion pumps
Suction machine
Defibrillator
Ventilator
Advanced Equipment
ABG machine
Portable X-ray
Ultrasound
Dialysis machine
Crash cart
Staffing Pattern in ICU
Medical Staff
Intensivist (1 per shift)
Resident doctors
Specialists (on call)
Nursing Staff
1:1 ratio (ventilated patient)
1:2 ratio (stable ICU patient)
Paramedical Staff
Respiratory therapist
ICU technician
Pharmacist
Dietician
Support Staff
Housekeeping
Biomedical engineer
Security
Support Services Required
Laboratory (24×7)
Blood bank
Radiology
Pharmacy
CSSD
Biomedical maintenance
Ambulance service
Quality Parameters for ICU
Structure Indicators
Bed occupancy rate
Nurse-patient ratio
Availability of equipment
Process Indicators
Hand hygiene compliance
Antibiotic policy adherence
Ventilator bundle compliance
Outcome Indicators
Mortality rate
Ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) rate
Average Length of Stay (ALOS)
Readmission rate
Quality of Process
Standard Treatment Protocols (STP)
Checklists (central line bundle)
Infection control policy
Medication safety protocol
Documentation standards
Quality of Outcome
Survival rate
Reduced infection rate
Reduced complications
Patient satisfaction
Ethical end-of-life decisions
Policies & Procedures in ICU
Admission & discharge policy
Infection control policy
Code blue policy
Biomedical waste management policy
Medication administration policy
Visitor policy
Restraint policy
End-of-life care policy
Evaluation of ICU Services
Methods
Clinical audit
Mortality review meetings
NABH standards compliance
Patient feedback analysis
Incident reporting system
Tools
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Root Cause Analysis (RCA)
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)




Comments