Bio Medical Waste Management
BIO MEDICAL WASTE MANAGEMENT
 Description also available in video format (attached
below), for better experience use your desktop.
Description also available in video format (attached
below), for better experience use your desktop.Introduction
·
BMWM is the management
of the waste that is generated during the diagnosis and treatment of a patient
·
Hospital Waste entirely divide into the below
mentioned categories
o
Non Hazardous (80%)
o
Hazardous (20%)
§ Infectious (15%)
§ Other Hazardous (5%)
· Non sharps
· Sharps
·
BMW can easily affect out the entire
community such as
o
Patients
o
Healthcare Workers
o
Municipal Workers
o
Rag pickers
o
Workers in recycling industries
BMW
Handling & Management Rules 2016
·
RULE 1 (SHORT TITLE AND COMMENCEMENT)
o
Bio-Medical Waste Management Rules, 1998
o
Came into force on the 20th July
1998
·
RULE 2 (APPLICATION)
o
Rules apply to all persons who
§ Generates, Collect, Receive, Store
§ Transport, Treat, Dispose & Handle the BMW
o
Rules shall not apply to
§ Radioactive Waste
§ Hazardous Chemicals
§ Lead acid batteries
§ E-waste
·
RULE 3 (IMPORTANT DEFINITIONS)
o
BMW:- Waste
that is generated during
§ The diagnosis, treatment or immunization of human being
or animals
§ In research activities
§ In the production or testing of biological
§ In health camps
o
Occupier
§ Person having control on an institution generating BMW
o
Authorization
§ Permission granted by the prescribed authority
o
BMW treatment facility
§ Facility that is used to treat and dispose the BMW
·
RULE 4 (DUTIES OF OCCUPIER)
o
Immunize all its healthcare workers
o
Establish a GPS enabled barcode system for
bags carrying BMW to outside the primises
o
Reports major accidents relating to BMW to
the SPCB (State Pollution Control Board)
o
Maintain the BMWM register
o
Display the BMWM monthly data on its website
o
ETP & STP installation
o
Form a committee to monitor and implement the
rules in his healthcare facility
·
RULE 5 (DUTIES OF OPERATOR)
o
Ensure the timely collection of BMW
o
Assist the occupier in conduct of training
·
RULE 6 (AUTHORITIES)
o
Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate
Change
o
Government of India
o
Ministry of Health & Family Welfare
o
Ministry of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary
o
Ministry of Defence
o
Central Pollution Control Board
o
State Pollution Control Board
o
Municipalities, Urban local bodies and Gram
Panchayts
·
RULE 7 (TREATMENT AND DISPOSAL)
o
Common treatment & disposal service will
be given with the range of 75km radius for all the healthcare facilities
o
If the service is not available, the occupier
can establish its own treatment & disposal facility by using
§ Incinerator
§ Autoclave
§ Microwave
§ Shreder
·
RULE 8 (SEGRIGATION, PACKAGING, TRANSPORTATION &
STORAGE)
o
Segregation should be done in containers or
bags at the point of generation
o
Then bags should be labelled as specific
during their packaging
o
The operator of the common facility shall
transport the BMW from the premises of the occupier
o
BMW shall not be stored beyond 48 hours and
if that is happen in any case of urgency, the occupier must inform it to the
SPCB
·
RULE 9 (PRESCRIBED AUTHORITY)
o
The prescribed authority shall be the SPCB
& Pollution Control Committees
·
RULE 10 (PROCEDURE OF AUTHORIZATION)
o
Application shall be made by the Occupier in
Form II to the Prescribed authority
o
Prescribed Authority will grant the
authorization in Form III
·
RULE 11 (ADVISORY BOARD)
o
For the State government a committee shall be
constituted under the chairman ship of Health Secretariat
o
For the Ministry of Defence a committee shall
be constituted under the Director General of Health services
·
RULE 12 (MONITORING OF IMPLEMENTATION)
o
Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate
change shall review the implementation of rules in the country
o
State government shall constitute a District
Level Monitoring Committee under the chairmanship of DM
o
This committee shall report to the SPCB for
taking further necessary actions
·
RULE 13 (ANNUAL REPORT)
o
Submitted by the occupier to the Prescribed
authority in Form IV on or before the 30th June of every year
o
Prescribed authority shall compile, review
and analyze the information received and send this information to CPCB on or
before the 31st July of every year
o
CPCB to MOEF on or before 31st
August every year
·
RULE 14 (MAINTENANCE OF RECORDS)
o
Records will be maintained by the authorized
person of
§ BMW generation
§ BMW collection
§ BMW receiving
§ BMW storage & transportation
§ BMW treatment & disposal
·
RULE 15 (ACCIDENT REPORTING)
o
Informed by the authorized person to the
Prescribed authority
o
The accident report must be forwarded within
24hrs along with the remedial steps taken in Form-V
·
RULE 16 (APPEAL)
o
In Form V, any person can appeal against the
prescribed authority to the State Secretary within 30 days
·
RULE 17 (SITE FOR COMMON BMW TREATMENT AND DISPOSAL
FACILITY)
o
The department in the business allocation of
land assignment shall be responsible for providing suitable site for it to the
State government
·
RULE 18 (LIABILITY OF AN OCCUPIER OF COMMON FACILITY)
o
All the damages caused to the environment or
public because of improper BMW handling
o
The actions will be taken under section 5
& 15 of this Act (1 Lakh fine/5years Imprisonment)
Classification of BMW
Categorization of BMW
·
Segregation
o
·
Collection
o
Segregated BMW in small bins get collected by
the housekeepers in the large size color coded bags
o
The bags get tied up and placed on a common
trolley to transport them at the storage site
o
Bags also have a bar code on it, to get
scanned
o
Bags must have the symbols of Biohazard &
Cytotoxic on it
o
Then these bags moves from the site of
generation & segregation to the site of storage from a separate route
o
At the storage site, these bags get stored in
the separated chambers made as per the instruction of BMW Act
·
Transportation
o
Special vehicles shall be used to transport
untreated wastes
o
The medium of transportation should be
covered
o
Avoid manual loading
o
Ensures the availability of signed document
by Nurse/Doctor before transportation having
§ Date
§ Shift
§ Quantity
§ Destination
o
Driver must be trained to accidental cases
·
Disposal/Treatment
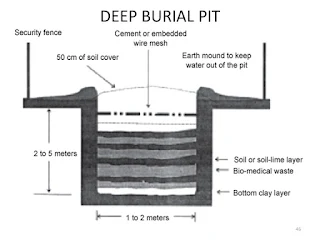
Deep
Burial Standards
·
Dug a pit of about a 2meter deep
·
Should be half filled with waste and covered
with lime upto the 50cm of space
·
Ensures that animals don’t have any access to
the burial sites
·
Use galvanized iron or wire meshes
·
Every time whenever waste is added to the
pit, a layer of 10cm of soil shall be added to cover the wastes
·
Burial site should be
o
Impermeable
o
Non shallow
o
Distant from habitation
o
Away from surface water
o
Away from prone, flooding and erosion area
·
Location shall be authorized by the
prescribed authority
·
Institution should maintain a record of all
pits used for deep burial
·
Ground water level should be a minimum of six
meters below the lower level of deep burial pit
BMW
Management Process
· .
Methods
of Disinfection
·
Incineration
o
High temperature dry oxidation process
o
Reduces organic and combustible waste into
inorganic incombustible matter like
§ Heat
§ Fuel gas
§ Ash
o
Results in significant reduction in waste
volume and weight
o
Generally selected to treat the waste that
cannot be
§ Recycled
§ Reused
§ Disposed in land
o
Basically of 3 types
§ Double Chambered (for infectious waste)
§ Single Chambered (when double chambered not affordable)
§ Rotator kilns (for toxic waste)
·
Chemical Disinfection
o
Used to treat liquid infectious waste like
§ Blood
§ Urine
§ Stool
§ Hospital Sewage
o
Chemicals are added in waste for killing or inactivate
the pathogen it contains
·
Wet & Dry Thermal Treatment
o
Wet thermal disinfection is based on the
exposure of waste to the high temperature by using steam
o
Wet disinfection cannot be used to treat
§ Anatomical Waste
§ Chemical Waste
§ Pharmaceutical Waste
o
In dry disinfection the waste is shredded and
heated in rotating auger
o
It can reduce 80% volume and 20-35 weight of
the waste
o
Suitable for infectious waste and sharps
·
Microwave Irradiation
o
Used to treat the waste by using
§ Frequency of 2450MHZ
§ Wave length 12.24cm
o
Destroy the microbes up to 99.99%
o
Rapidly destroyed the water contained
infectious waste by heat conduction
·
Land Disposal
o
Use of Open Dumps to treat the waste
o
A risk for public health in Open Dumps
o
Another way of land disposal is Sanitary landfills
§ Design and constructed to prevent contamination of
· Soil
· Surface
· Ground
· Water
· Direct contact with public
·
Inertization
o
Process of mixing waste with cement before
disposal
o
It minimizes the risk of toxic substance
migrating into the water surface
o
It prevents scavenging
o
The proportion that is generally used is
§ Waste 65%
§ Lime 15%
§ Cement 15%
§ Water 5%
Modern
Technology for Handing BMW
·
Steam Sterilization
o
Also known as autoclaving
o
Most common alternative treatment method
o
Worked on the principle of doing steam
sterilization in closed chamber where both heat and pressure are applied over a
period of time to destroy all microorganisms
o
Always performed before the landfill disposal
of BMW
o
This process has the
§ Lowest capital cost
§ Used to process 90% of medical waste
§ Easily scaled to meet the needs of any medical
organizations
·
Advanced Autoclaves
o
A combine steam treatment with
§ Vacuuming
§ Internal mixing
§ Fragmentation
§ Internal Shredding
§ Drying
§ Compaction
o
It leads to the 90% volume reduction of the
waste
o
Have higher capital cost
·
Microwaves
o
A promising medical waste disposal technology
o
Treatment of waste occurs through the use of
moist heat and steam generated from microwave energy
o
It consist of a treatment chamber inside
which the microwave energy is directed from a microwave generator
o
Have higher capital cost
o
Can be batch or semi-continuous in nature
·
Chemical Process
o
Use disinfectants such as lime or peracetic
acid to treat the waste
o
The heated alkali easily digests the
§ Tissues
§ Pathological waste
§ Anatomical parts
§ Animal Carcasses
o
The whole process takes place inside a
stainless steel chamber
o
Have a low capital cost
·
Plasma Gasification
o
An emerging and promising option to dispose
medical waste
o
It uses an oxygen starved reactor that is
operated at a high temperature and results in the breakdown of waste into
§ Hydrogen
§ Carbon monoxide
§ Water etc
o
Main product of Plasma gasification is Energy
rich gases
o
These gases can be converted into
§ Heat
§ Electricity
§ Liquid fuels
Monitoring
& Controlling Cross Infection
·
Monitoring Techniques
o
Designate an Infection Control Owner
§ The basic and compulsory need for any monitoring is a
supervisor
§ She/he is responsible to monitor the each and every
aspect that contributes to control the cross infection
§ The controlling officer can be the Infection Control
Nurse
§ She is used for the distribution of specific task to a
specific person
§ It increases the chances of staying compliant
o
Dedicate the Necessary Resources
§ Like every other area of hospital, infection control area
also needs proper resources like
· Time
· Money
· Material etc
§ For an effective monitoring we need the resources to
implement the policies and to decrease the cross infection
o
By developing an Infection Control Committee
§ Responsible for the monitoring program and policies
§ Used to implement the SOPs
§ Recommend the corrective actions
·
Controlling Methods
o
Hand hygiene
o
Environmental hygiene
o
Patient screening
o
Cohorting patients
o
Surveillance
o
Antibiotic stewardship
o
Follow guidelines
o
Safety culture
o
Use of Personnel Protective Equipments
§ Mask
§ Face shield
§ Gloves
§ PPE kit
§ Gown
§ Utility gloves
o
Immunization against communicable diseases
o
Restrict visitors
o
Isolation
o
Proper ventilation
Waste
Reduction Activities for a Hospital
·
Develop a formal waste disposal management
plan
·
Give thorough & consistent employee
training
·
Clearly understand the rules & norms of
BMW
·
Restrict access whenever possible
·
Maintain physical separation between different
waste bins
·
Use color code containers to ensure appropriate
sorting
·
Post strategic signage
·
Conduct waste audits
·
Keep an eye on pharmaceutical agents
·
Recycling & Reuse
BMW
Awareness & Education
·
At present the awareness and education about
the BMW is a compulsion for the entire community
·
Not even the hospital but the whole community
must have to understand that the medical waste is directly or indirectly
related to their health
·
BMW affects the entire community but the
population which are at greatest risk
o
Patients
o
Healthcare workers
o
Municipal workers
o
Rag pickers
o
Workers at recycling industries
o
Workers at treatment facilities
·
The awareness and education on BMW can be
conducted out via
o
Training on regular basis
o
Run social media contest
o
Pursue local partnership
o
Create info graphics
o
Nukkad Natak
o
Publishing articles on BMW in newspapers
Video
Description
·
Don’t forget to do
these things if you get benefitted from this article
o
Visit our Let’s
contribute page https://keedainformation.blogspot.com/p/lets-contribute.html
o
Follow our page
o
Like & comment
on our post
·










Comments
Telemedicine App Development Company